Inspecting Docker container network traffic
posted in docker
When developing dockerized services with other communication end-points than browser client one soon needs some ways to capture and debug network traffic from containers. Here’s some tools and tips I’ve been using.
Capturing traffic
Docker uses network bridge for all traffic, and by default containers will be
using bridge named docker0. However if you are using docker-compose, which
by default creates own bridge for each configuration or you have other ways to
configure docker networking the bridge you would like to capture would be
different.
Use docker network ls command to list available Docker networks with the help
of bridge link and ip addr show to find correct interface for your use case.
Rest of this post will be using default docker0.
Docker Documentation for container networking has more details, and information for custom configurations.
Using tcpdump
Tcpdump is versatile commandline tool for capturing and analyzing network traffic. Try following to listen your containers:
tcpdump -i docker0
Or record traffic to a file:
tcpdump -i docker0 -w packets.cap
You could also use Wireshark which is GUI tool for analyzing
traffic, and it could be also used to view output from tcpdump.
There’s still one problem though. Any sane service handling personal data should encrypt its communication preventing debuggin with simple packet capturing. To view encrypted TLS traffic we would need Man-in-the-middle transparently decryptin and re-encrypting traffic.
Setting up transparent HTTP(S) proxy
For man-in-the-middle setup we need following:
- Proxy
- IP packet forwarding to redirect traffic to proxy
- Configure CA certificates from proxy as trusted by the service we are examining
Mitmproxy is a perfect tool for this job.
Packet forwarding and Mitmproxy setup
-
See Mitmproxy documentation for installation options or run it using official Docker images
-
Enable packet forwarding in your host system with sysctl:
sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 -
Use
iptablesto forward interesting traffic from bridge to proxy. Following will forward HTTP targeting default port 80 and HTTPS to default port 443 to proxy running in 8080 which is Mitmproxy default.iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i docker0 -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-port 8080 iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i docker0 -p tcp --dport 443 -j REDIRECT --to-port 8080 -
Run mitmproxy in transparent mode:
mitmproxy -T --host
Configure CA certificates
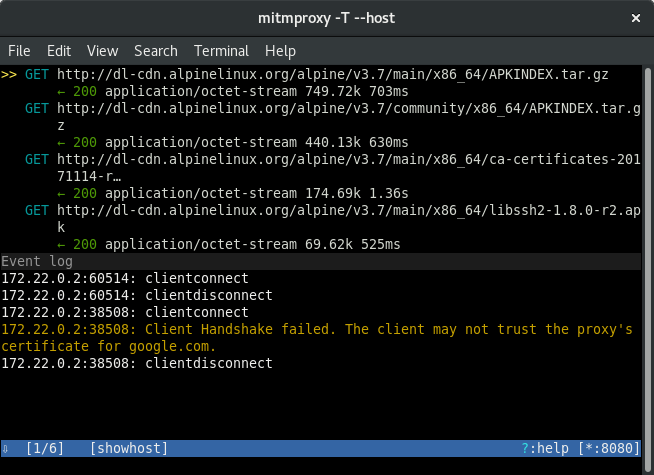
Now HTTPS clients configured to verify server certificates would fail connecting, which will look like following in then Mitmproxy event log:
Mitmproxy generates its CA to directory $HOME/.mitmproxy, which could be
mounted as a volume to your Docker container. If your are using Docker to run
Mitmproxy you would mount volumes from that container.
docker run --volume $HOME/.mitmproxy:/usr/share/ca-certificates/custom some-image
Rest depends on used Linux distribution and service implementation you are targeting:
-
For Unix system tools in Alpine Linux based containers:
-
Mount custom certificates under some dir eg.
customat/usr/share/ca-certificatesdocker run -v ~/.mitmproxy:/usr/share/ca-certificates/custom ... -
Add
custom/mitmproxy-ca-cert.pemto/etc/ca-certificates.confin your containerecho custom/mitmproxy-ca-cert.pem >> /etc/ca-certificates.conf -
Update trusted root certificates by running:
update-ca-certificates
-
-
NodeJS has support for
NODE_EXTRA_CA_CERTSenvironment variable since v7.3.0docker run --volume $HOME/.mitmproxy:/opt/extra-ca \ -e NODE_EXTRA_CA_CERTS=/opt/extra-ca/mitmproxy-ca-cert.pem nodejs -
Ruby OpenSSL uses system root certs or they could be overriden with
SSL_CERT_FILEandSSL_CERT_DIRenvironment variables -
For example Go, Elixir, Python based implementations would use system root certificates
After these steps it is possible to examine TLS traffic.
Extra tricks with mitmproxy
Possibilities with Mitmproxy are not limited to just inspection. For example see official documentation for how to edit request or response before letting it go through proxy to client or server.